|
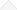
Andaman & Nicobar Islands are a group of islands located on the coast of the Bay of Bengal, consisting of more than 572 islands of which approximately 37 islands are inhabited. The archipelago is the home of diverse flora and fauna and is the only region of several species and also home to a few indigenous communities like the Great Andamanese, Onge, Jarawa, Sentinelese, Shompens, and Nicobarese tribes.
Let’s understand the facts about Andaman & Nicobar Islands more elaborately:
1. Geographical facts
2. History and Origin of the Islands
3. Unique Flora and Fauna
4. Indigenous Communities
5. Adventure and Recreational Activities
6. Environmental Protection and Conservation Efforts
7. Economic Significance
8. Notable Places to Visit
9. Cultural Diversity
10. Contemporary Issues and Challenges.
1.Geographical facts: The geographical facts make the Andaman and Nicobar Islands a unique and beautiful region, with a rich and diverse ecosystem that is of great significance to India and the world.
- Archipelago: The Andaman & Nicobar Islands is an archipelago in which there are 572 islands and only a few of them are inhabited.
- Area: The Andaman and Nicobar lies between 6° 44' to 14° 50' North latitude and 92° 06' to 94° 25' East longitude.
- Climate: The climate in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands is tropical, where the temperature ranges from 25°C to 35°C from November to May and the islands receive heavy rainfall from June to September, during the monsoon season and the temperature ranges between 19°C to 28°C.
- Seas: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are surrounded by the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Andaman Sea to the south.
- Seismic Zone: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are located in a seismically active zone and are vulnerable to earthquakes and tsunamis.
- Natural resources: The Andaman & Nicobar Islands are rich in natural resources like timber, coconut, and rubber and also known for their marine life like flora & fauna, coral reefs, seaweeds, and diverse species of fish.
2. History and Origin of the Islands: The history of Andaman & Nicobar Islands are rich and diverse because of some factors like:
- Early Inhabitants: The earliest known inhabitants of the islands were the Great Andamanese, and it is believed that they lived on the islands for over 26,000 years.
- Colonial Era: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands have a history of colonial rule by some major powers including the British, Japanese, Dutch, and French.
- Freedom Struggle: During the freedom struggle of India, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands played a major role in which the well-known Cellular Jail use to be the darkest prison for Indian Political leaders.
- Post-Independence: After India got independence from Britain in 1947, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands were declared as one of the Union Territory of India.
- Development: A significant increase in tourism and economic activity has been seen in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, with efforts being made to improve infrastructure and promote conservation and environmental protection.
3. Unique Flora and Fauna: The Andaman & Nicobar Islands are well known for the unique and diverse flora and fauna found in the region.
- Flora: The Andaman & Nicobar Islands have a variety of tropical forests like mangrove forests, tropical evergreen forests, and tropical moist deciduous forests. The native tree of Andaman Islands is Andaman Padauk.
- Fauna: The Andaman & Nicobar Islands are the home of many wildlife and a heavy range of species like the saltwater crocodile, giant leatherback turtle, and several species of primates. The islands are also home to a variety of bird species, including the Andaman serpent eagle, Andaman wood pigeons, and the Andaman scops owl.
4. Indigenous Communities: The Andaman & Nicobar Islands have varieties of tribe communities and each is very rich in culture and traditions.
- Great Andamanese: The Great Andamanese are the earliest known inhabitants of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, with a residing history of over 26,000 years. The Great Andamanese are known for their traditional dances and music.
- Onge: The Onge are one of India’s most isolated indigenous communities and are native to Little Andaman Island. The Onge are known for their traditional hunting and gathering practices.
- Jarwa: The Jarwa is an indigenous community native to the Middle and South Andaman Islands. The Jarwa are known for their traditional hunting and fishing practices.
- Nicobarese: The Nicobarese are an indigenous community native to the Nicobar Islands. The Nicobarese are known for their traditional fishing and hunting practices and their use of palm fronds for constructing homes.
5. Adventure and Recreational Activities: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands offer a variety of adventure and recreational activities, making it a popular destination for tourists and adventure enthusiasts.
- Water Sports: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are popular destinations for water sports, including scuba diving, snorkeling, surfing, and sea kayaking.
- Trekking: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are also popular destinations for trekking, with several well-established trails leading through the islands’ lush tropical forests and hills.
- Wildlife Safaris: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are home to a diverse range of wildlife, including several species of primates, birds, and reptiles. Wildlife safaris offer a unique opportunity to observe and learn about the wildlife of the islands.
- Beach Activities: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are also known for their pristine beaches, with a variety of activities available including sunbathing, swimming, and beach volleyball.
- Cultural Activities: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are also a hub of cultural activity, with several museums, historical sites, and cultural festivals taking place throughout the year.
6. Environmental Protection and Conservation Efforts: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are a rich and diverse ecosystem, with unique flora and fauna and several indigenous communities, there have been significant efforts made to protect and conserve the environment of the islands.
- Marine National Parks: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are home to two marine national parks, the Mahatma Gandhi Marine National Park and the Campbell Bay National Park.
- Wildlife Sanctuaries: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are also home to several wildlife sanctuaries, including the Galathea National Park, which is home to a variety of wildlife like the saltwater crocodile and the giant leatherback turtle.
- Forest Conservation: These areas play an important role in conserving the unique and diverse flora and fauna of the islands. Significant efforts have been made to conserve the forests of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, with large areas of the islands designated as protected forest areas.
- Community Conservation: The indigenous communities of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands play an important role in the conservation and protection of the environment, to ensure their continued involvement in the conservation of the islands’ ecosystem.
7. Economic Significance: The Andaman & Nicobar Islands have several industries and sectors which play a major role in the economic development of the country, India, and also provide employment opportunities and generate revenue for the region. Some of the economic areas are mentioned below:
- Tourism: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are popular tourist destinations, attracting millions of visitors each year. The tourism industry is a significant contributor to the local economy, providing employment opportunities and generating revenue for the region.
- Fishing: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are also an important hub for the fishing industry that provides livelihoods for the local communities and contributes to the local economy.
- Agriculture: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are home to the agricultural sector, with crops such as rice, coconut, and spices being grown and harvested for local consumption and export.
- Timber Industry: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are also home to a timber industry, with the production and export of timber and related products playing an important role in the local economy.
- Shipping and Logistics: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are strategically located, making them an important hub for shipping and logistics in the Bay of Bengal and the Indian Ocean.
8. Notable Places to Visit: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are home to stunning natural beauty and rich cultural heritage, making them a popular destination for tourists. Some of the most notable places to visit in the islands include:
- Havelock Island: This is the most popular tourist spot destination in the archipelago, having Asia’s no. 1 beach i.e., Radhanagar Beach which is the most beautiful beach on the island, popular for its crystal clear water, white sands, and mesmerizing sunset views.
- Ross Island: It is a small island, an earlier British Colonial administrative center with churches, ballrooms, bakery, buildings, etc., and is now declared a famous tourist spot by the local administration.
- Neil Island: A island 43km away from the main Port Blair Island, famous for its beaches, water activities, and natural coral bridge.
- Corbyn’s Cove Beach: A beautiful beach within 10km away from the main city and a perfect place for water adventurous activities.
- Baratang Island: It is an island beautiful for its natural landscapes, Limestone cave, and Mud volcano, Parrot island, has to pass through a dense tropical forest area reserved for the Jarawa community tribes.
9. Cultural Diversity: The cultural diversity of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a result of the unique history and geography of the region. The cultural richness of the islands has contributed to the development of a vibrant and diverse community that celebrates the traditions and heritage of the region.
10. Contemporary Issues and Challenges: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands has several contemporary issues and challenges, including:
- Environmental degradation: The islands are known for their unique and fragile ecosystem, and there are concerns about the impact of industrial and commercial development on the environment. This includes issues such as deforestation, water pollution, and loss of biodiversity.
- Infrastructure development: The rapid pace of development in the islands has led to several infrastructure-related challenges, including the need for better roads, transportation, and housing.
- Health and medical facilities: The remote location of the islands presents challenges in terms of accessing adequate healthcare facilities. There is a shortage of doctors, nurses, and other medical professionals, and limited access to specialized care.
- Education and employment: Despite recent efforts to improve the educational infrastructure of the islands, there are still challenges in terms of access to quality education and job opportunities for the local population.
- Cultural preservation: The indigenous tribes of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands have unique cultures and traditions that are at risk of being lost as a result of outside influence and development. There are ongoing efforts to preserve and promote the cultural heritage of the tribes.
- Disaster management: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are located in a region that is prone to natural disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, and tropical cyclones.
Conclusion:
Andaman and Nicobar Island, A Perfect Island Archipelago in the Indian Sea with the most amazing and breathtaking views and experiences that can blow your mind. Andaman offers you a wide range of things to explore and drag you from your daily city hustles. If you want a break from your daily stressed life and have a holiday, then plan it for Andaman.
|